The MOVE Index as a Predictor of Market Volatility and Financial Distress
The MOVE Index tracks U.S. interest rate volatility and can provide an early signal of shifting risk sentiment in the bond market and the wider financial markets, before it shows up in equities.
Key Takeaways
-
MOVE is like the VIX for bonds, with a strong track record of reflecting bond market sentiment (🔗 Treasury Bills)
-
MOVE can be used alongside the VIX (explained later) to gauge overall market risk and investor sentiment.
- The bond market often signals major changes before the equity market.
Introduction to the MOVE Index
Created in 1988, MOVE stands for ‘Merrill Lynch Option Volatility Estimate’ and is designed to track U.S. Treasury yield volatility implied by current prices of 1-month OTC options.
-
The MOVE Index measures U.S. Treasury yield volatility based on 1-month OTC options.
-
Intercontinental Exchange (NYSE: ICE) acquired MOVE from Bank of America Merrill in 2019, along with a family of fixed-income volatility indices.
-
Volatility is measured for 2-year, 5-year, 10-year, and 30-year U.S. Treasuries.
-
The average reading since inception is around 103.
How the MOVE Index Relates to the VIX and U.S. Stocks
A spike in both VIX and MOVE reflects turmoil in the financial markets. Conversely, low readings on both indexes indicate normal market conditions.
-
Both MOVE and VIX are based on options pricing.
-
Both calculate 1-month volatility.
-
MOVE and VIX tend to be closely correlated (0.80).
What Is the VIX (Cboe Volatility Index)?
VIX is a real-time index that reflects the market’s expectations for S&P 500 volatility over the next 30 days. Investors closely watch it, as it has historically provided reliable insight into equity market risk.
Chart: The correlation between MOVE and VIX (monthly chart)

The correlation between the bond and equity markets
Historically, the bond and equity markets are correlated, largely because changes in interest rates affect both.
-
When interest rates rise or are expected to rise, bond and equity prices generally fall.
-
When interest rates fall or are expected to fall, bond and equity prices generally rise.
-
Other factors can influence both markets in the same direction, such as political risk, business risk, and legislation that affects capital flows.
The chart below shows that the MOVE Index tends to peak during turbulence in the S&P 500.
Chart: The correlation between MOVE and the S&P 500
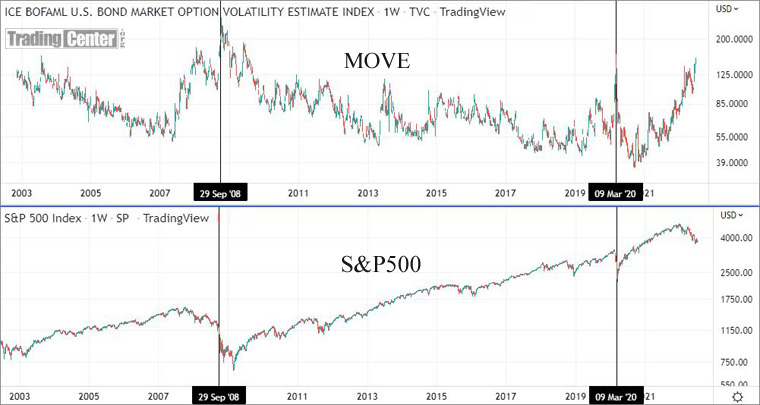
◘ Linking Interest Rate Volatility to Equity Markets: The MOVE Index and the S&P 500
G.P. for TradingCenter.org (c) July 2022
🔗 MOVE Index Links:
- https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/%5EMOVE/
- https://markets.ft.com/data/indices/tearsheet/summary?s=MOVE:PSE
L MORE TUTORIALS • GENERAL GUIDES • TECHNICAL ANALYSIS
□ Equity Trading
» TD Sequential
» Wyckoff's Method
• FUNDAMENTAL ANALYSIS
» Money Supply & Liquidity
» Dow Theory & Strategy
» P/E, PEG, and Shiller P/E
» Warren Buffett’s Method
» Zweig Breadth Thrust Signal
» Benner’s Cycle
» Stock Market Formula
» MOVE Volatility Index


