〽️ MAJOR TYPES OF TECHNICAL ANALYSIS CHARTS

Technical analysts rely on charts to identify price action and spot strong trends, patterns. The four main types of charts they use include: (1) Line, (2) Bar, (3) Candlestick, and (4) Point & Figure.
There are also less common charts such as the Renko Chart (ignores time) and Heikin-Ashi Chart (Smoothed candlesticks filtering market noise)
![]() Introduction to the Four Major Types of Charts
Introduction to the Four Major Types of Charts
Technical analysis charts provide a visual representation of an asset’s price movements to help identify trends and patterns. The four main types are:
-
Line Charts: Connecting closing prices over time with a continuous line, offering a straightforward view of overall trends.
-
Bar Charts (OHLC): Each bar shows the Open, High, Low, and Close prices for a period, with vertical bars and horizontal ticks that reveal price volatility.
-
Candlestick Charts: Using color-coded bodies—typically green or white for upward closes and red or black for downward—along with wicks that mark price highs and lows, these charts highlight market sentiment and pattern formations.
-
Point & Figure Charts: These focus solely on significant price changes, plotting columns of Xs for rising prices and Os for falling ones, ignoring time intervals to emphasize major trends by filtering out minor fluctuations.
The table below compares the four major types of charts.
Table: Key Comparisons Between Chart Types
| Chart Type | Data Shown on the Chart | Suitable Use | Trading Styles |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Only closing prices |
|
|
|
Opening-High-Low-Closing prices |
|
|
|
Openning-High-Low-Closing prices + market sentiment |
|
|
|
Filtered price movements |
|
|
(1) Line Chart
A line chart shows the daily closing prices of financial securities. It’s useful for spotting long-term trends and comparing related financial variables—for example, comparing an oil company’s stock price with the price of oil over a period.
Structure:
- A single continuous line connecting closing prices.
(2) Bar Chart
A bar chart is often used to track short- and mid-term price movements. It shows the daily open, close, high, and low prices. The left dash shows the opening price, the right dash shows the closing price, the top of the bar is the daily high, and the bottom is the daily low.
Structure:
-
Vertical bar: High to Low range.
-
Left tick: Opening price.
-
Right tick: Closing price.
If the opening price (left dash) is lower than the closing price (right dash), the bar is colored black. If the opening price is higher than the closing price, the bar is colored differently (the text cuts off here).
(3) Candlestick Chart
Candlestick charts, originating from Japan, are widely used in the Forex market. A candlestick chart combines features of both line and bar charts. Each candlestick shows the full price range of a financial security during a set period. Like a bar chart, it includes a thin vertical line representing the trading range.
Structure:
-
Body: Rectangle between open/close prices.
-
Green/white body: Close > Open (bullish).
-
Red/black body: Close < Open (bearish).
-
(4) Point and Figure Chart
Point and Figure Charts focus on price movements and pay less attention to time and volume. They use Xs to show rising prices and Os to show falling prices. Numbers and letters in the chart indicate time, such as months.
Structure:
-
X-columns: Represent rising prices.
-
O-columns: Represent falling prices.
-
Box size: Minimum price change needed to add a new X or O.
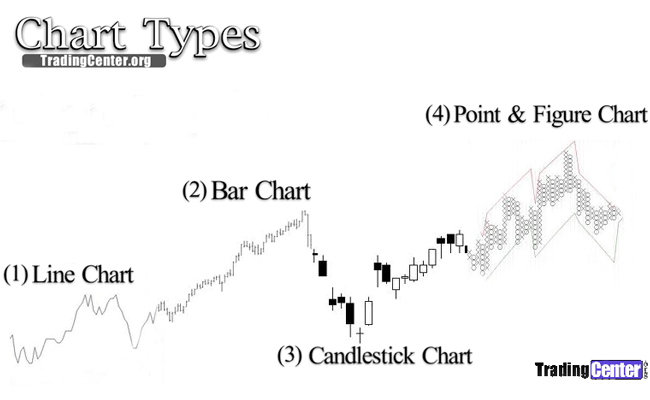
〽️ Comparing Chart Types
The graph below shows the four main chart types: Line, Bar, Candlestick, and Point and Figure charts. Here are some key points to remember:
✅ Choose your chart timeframe based on your goal (daily, weekly, or monthly to best fit your investment horizon and objectives).
✅ Select chart types that suit your trading style -for instance, candlestick charts work well for day traders, while Point & Figure charts are often preferred by long-term investors.
✅ Enhance your trading analysis by combining charts with indicators like MACD or RSI for more reliable signals.
Graph: The four main chart types
![]() Charting Indicators & Key Price Points on any Chart
Charting Indicators & Key Price Points on any Chart
Here are the three most common chart indicators:
□ Moving Averages (MA): These smooth price changes by averaging prices over set periods (like 50-day or 200-day), helping to identify trends. Trend changes often happen when a short-term MA crosses above or below a long-term MA—such as the famous “Golden Cross.”
□ Relative Strength Index (RSI): This momentum indicator ranges from 0 to 100 and signals overbought levels above 70 or oversold levels below 30, which can indicate possible price reversals.
🔗 More: » RSI Precision v.3 (Multisignal Indicator)
□ Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): This measures trend strength and possible reversals by comparing two exponential moving averages (12-period and 26-period) and a 9-period signal line. The MACD uses histogram bars to show momentum shifts, especially when the MACD line crosses the signal line.
Key chart levels on any chart:
-
Resistance Point – Above the current price, it marks a level where selling may increase.
-
Support Point – Below the current price, it marks a level where buying may increase.
-
Breakout Point – The point where the price breaks support or resistance levels. At this point, volume usually rises, strengthening the current trend.
□ TradingCenter (c)
You are not allowed to publish, reproduce, translate, merge, sell, rent, or distribute any content on this website (TradingCenter). You are not also allowed to create a derivative work or utilize framing techniques to enclose any content on this website (TradingCenter).
L MORE ON TECHNICAL ANALYSIS • COMPARE • TECHNICAL ANALYSIS • INDICATORS • LEARNING
□ Forex Brokers Comparison
□ Expert Advisors (EAs)
□ Broker Reviews
□ Learning
» Technical Analysis Guide
» Trading Chart Patterns
» Harmonic Price Patterns
» Forex Technical Analysis
» Fibonacci Primes Sequence
» Naked Charts & Price Zones
» RSI Precision
» PriceMomentum Chart
» CVD Indicator
» Key Technical Indicators
» ΔMP and Σ(ΔMP) Indicators
» Forex Pairs
» Trading Books
» Trading Tips
» TD Sequential


